ACS applied Energy Materials: 2019, 2 (1), pp 788–796
Link
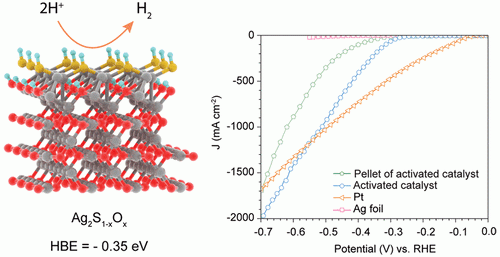
Abstract: One of the bottlenecks toward the successful implementation of alternative energies is the lack of methods for sustainable generation of hydrogen fuel as an energy carrier. Given that water will be at the very least an important component of the hydrogen production feedstock, sustainable catalysts are needed for the electrochemical generation of hydrogen from water. Herein, we report on the electrochemical activation of a silver-based catalyst for the efficient hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in acidic conditions at high current densities. After activation, the catalyst is chemically and electrochemically stable over days. The starting material, silver sulfide, is synthesized by a simple and scalable chemical vapor deposition process. Upon electrochemical activation, the pristine material is converted to mesoporous silver coated with a silver oxo-sulfide layer which is highly active toward HER. Detailed microscopy and spectroscopy demonstrate the formation of both hydroxyl and sulfoxide groups on the surface of the catalyst. Interestingly, the density functional theory calculations suggest that only in the presence of these hydroxyl groups will sulfur atoms exhibit high catalytic activity with a hydrogen binding energy of −0.35 eV.
Keywords:
electrocatalysis; electrolysis; hydrogen evolution reaction; nanomaterials; water splitting